LOCALISATION OF FUNCTION ASSESSMENT INCLUDING ESSAY WRITING
Localisation of function in the brain assessment and essay advice
BRAIN PLASTICITY AND FUNCTIONAL RECOVERY: REVISION BOOKLET
Assessment material for brain plasticity and functional recovery
WAYS OF INVESTIGATING THE BRAIN
How do we investigate the brain? From fMRI and EEG to post-mortem studies and electrical stimulation, explore the key techniques neuroscientists use to understand cognition and behaviour
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
The nervous system is divided into the central and peripheral systems, with the peripheral system further split into the somatic and autonomic branches. Discover how these divisions control everything from voluntary movements to automatic bodily functions
FIGHT OR FLIGHT
THE FIGHT OR FLIGHT RESPONSE, INCLUDING THE ROLE OF ADRENALINE: Explore how the nervous system responds to stress through the fight or flight mechanism. Understand the role of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS), including sympathetic arousal and the release of adrenaline to prepare the body for action.
ENDOCRINE AND HORMONES
Discover the function of the endocrine system, exploring how glands release hormones to regulate essential processes like stress, metabolism, and growth
RHYTHMS: CIRCADIAN, INFRADIAN AND ULTRADIAN
Learn about biological rhythms, including circadian, infradian, and ultradian cycles. Explore the role of endogenous pacemakers and exogenous zeitgebers in regulating the sleep/wake cycle and other vital processes.
BRAIN ANATOMY AND FUNCTION
Dive into brain anatomy and function, exploring the cortices, lobes, hindbrain, midbrain, forebrain, and the limbic system. Learn how these structures work together to control behaviour, emotions, and essential bodily functions.
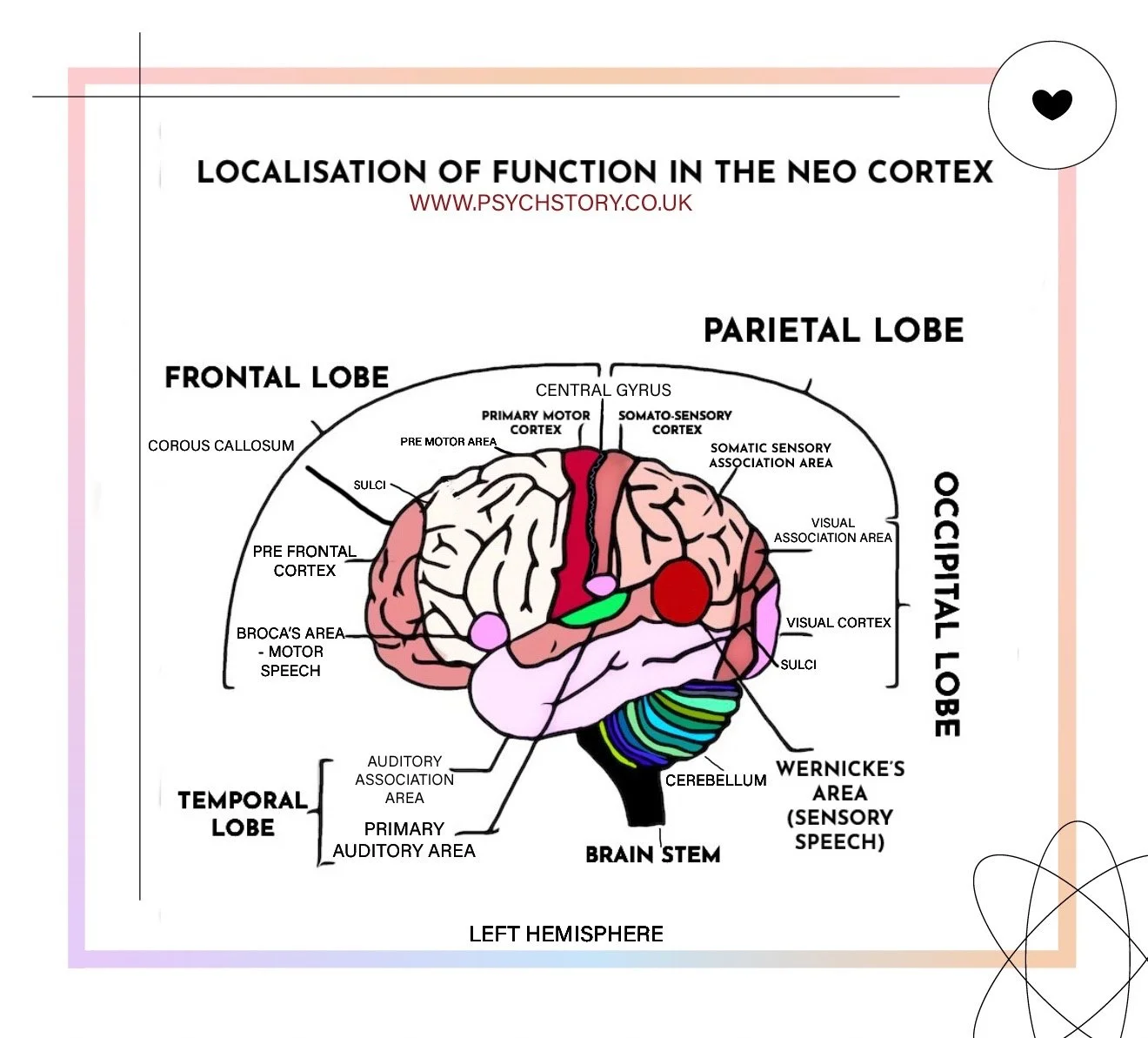
LOCALISATION OF FUNCTION IN THE BRAIN
Explore localisation of function in the brain, including the motor, somatosensory, visual, auditory, and language centres. Learn about Broca’s and Wernicke’s areas and their roles in speech and comprehension
HEMISPHERIC BRAIN LATERALISATION
Discover hemispheric lateralisation and how the brain’s hemispheres specialise in visual, auditory, and language processing. Understand how each hemisphere contributes uniquely to communication and perception
NEURO PLASTICITY AND FUNCTIONAL RECOVERY OF THE BRAIN
Neuroplasticity allows the brain to adapt and reorganise in response to experience, learning, and injury. Experience-expectant plasticity occurs during early development when the brain forms neural connections in response to environmental stimuli. Experience-dependent plasticity continues throughout life, allowing adaptation based on unique experiences. Functional recovery after trauma demonstrates the brain’s ability to compensate for damage, often through neural reorganisation and recruitment of undamaged areas. Explore the fascinating ways in which the brain adapts and recovers from injury
THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF NEURONS
Learn about the structure and function of sensory, relay, and motor neurons and how they transmit signals across the nervous system. Explore the process of synaptic transmission, including the role of neurotransmitters, excitation, and inhibition.
GENES AND HOW TO RESEARCH THEM
Explore genetic research methods, including twin, adoption, and genome-wide association studies (GWAS). Learn how these approaches uncover the influence of genetics on behaviour and health.
GLOSSARY OF THE BRAIN
Explore a detailed glossary of the brain, including the lobes, cortices, limbic system, and brainstem. Perfect for understanding brain anatomy and its complex functions.